Building high-fidelity spectrographs
While high resolution imaging has benefited tremendously from Adaptive Optics (AO) in the last decade (VLT NACO, SINFONI, MAD) and has allowed advances in the exoplanet field, radial velocity techniques have not. In the E-ELT area, it is now time to think the design of new radial velocity spectrographs together with an associated AO system that will allow to concentrate the starlight into a much smaller spot than when limited by the seeing and therefore will allow the fiber collecting the light to have a smaller core for the same light collecting efficiency.
Since the size of the input fiber essentially determines the size of the spectrograph, having a small fiber will allow to build smaller spectrographs that will be not only cheaper but also more stable thermo-mecanically.
In this sub-project,
- We scrutinize the design parameters of an AO system optimized to minimize the radius of the encircled energy at the telescope focus
- We will study new control algorithms for this purpose also
- We will design and build a test bench to validate the concept and study the performance limits as a function of different external paramers (seeing, wavelength of interest, star magnitude, etc…)
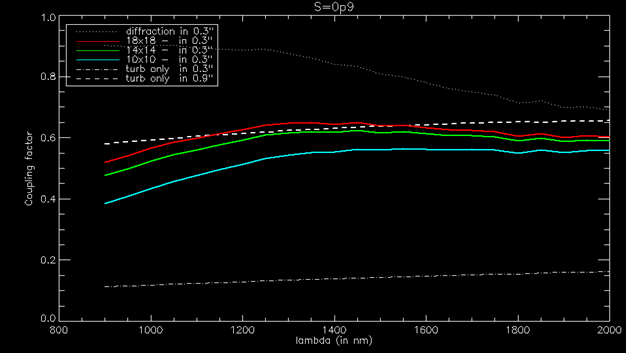
Encircled Energy (EE) in a 0.3″ fiber for different AO parameters in colors. For comparison we present seeing-limited performance with 0.9″ fiber (top white dashed line) and 0.3″ fiber (bottom white dashed line)




