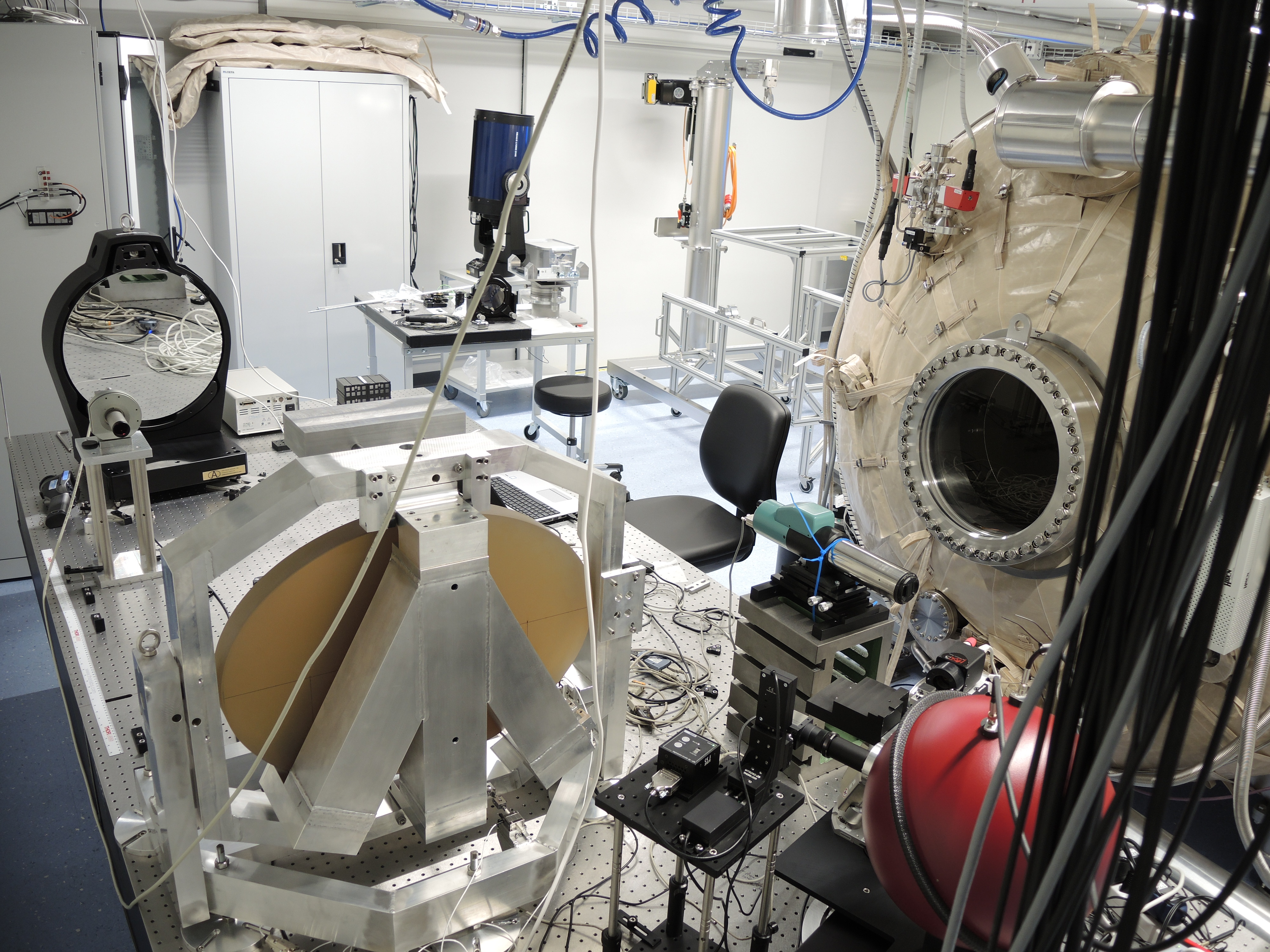
Integrating sphere. It must emit a uniform light beam over the surface of a disc. Two fibers (a and b) are connected thereto, for an incoming source (white or monochromatic) and the other outgoing to ensure the feedback loop of the ultra stable source.
Ultra stable source simulating a star.
Support the tip-tilt mirror (rotating along the 2 vertical and horizontal axes). This mirror is elliptical to send a uniform disk of light in the direction of the telescope.
Alignment Table of the photometer for measuring the flow of the integrating sphere and ultra stable source. (Up-down, left-right).
Photometer to measure the outflow of the integrating sphere and ultra stable source to allow their alignment.
Plateau to change the source of light that will illuminate the CCD, either the sphere or the star.
Laser Source to maintain the mirror in a good position.
Parabolic mirror to make parallel the rays of light beam leaving the integrating sphere or the ultra stable source.
Opening into the vacuum chamber containing CHEOPS so that light illuminates the integrated optics and the CCD.